Human Nervous System
The human nervous system comprises of central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central neervous system consist of brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consist of nervous from the brain and spinal nerves from the spinal cord. The structural and functional unit of nervous system is neuron.
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF NEURON
Neurons are long, thin delicate cells. A single neuron may extend from the spinal cord of the man to the foot. Bundles of neuron fibres are called nerves. The portion of the neuron most resembling other cells is the cell body. The cell body contains a nucleus and cytoplasm. The long fibre of a neuron leading away from the cell body is the axon. An axon transmits impulses away from the cell body. The other end of the neuron is a highly branched structure called dendrites. Impulses move toward the cell body from the dendrites and from cell body to axon.
Long neuron fibres are covered by fatty myelin sheath. Cells of myelin sheath are called Schwann cells. Smalls gaps between consecutive Schwann cells are called nodes of Ranvier. Both mylein sheath and the nodes of ranvier are important in determining the speed with which impulses are conducted. Mylein sheath is an insulator so the membrane coated with this sheath does not conduct nerve impulse. In such a neuron, impulse jumps over the mylein going from node to node. These jumping or saltatory impulses increase the speed of nerve impulse.
Types of Neurons
The neurons differ in structure and in direction toward which they carry impulses.
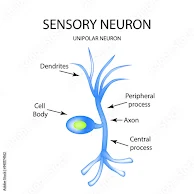
Sensory Neurons: They carry sensory information from receptor to the brain and spinal cord.
Motor Neurons: They carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the effectors. They have many dendrites and one axon.
Interneurons: These are found inbrain and spinal cord. They have many dendrites and axons. The interneuron carries impulses from sensory neuron to motor neuron.
COMPONENTS OF CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Here we will discuss the brain and spinal cord as the components of human nervous system.
Brain
It is enclosed within the cranium (Skull). The brain and the spinal cord are covered with three protective membranes called meninges. Between the inner and middle layer there is a fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, which helps to cushion the brain form shock. Meninges also provide nutrients and oxygen to brain tissue through capillaries. The brain contain hollows spaces called ventricles that are continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord. These are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Brain is divided in to three parts, forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain.
Forebrain
The forebrain consist of cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. Cerebrum, is largest main centre of various sensations e.g., hearing, sight smell, memory voluntary action, intelligence, and reasoning. Cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into four major lobes. Frontal lobes,Parietal lobe,Temporal lobe,Occipital lobe.
Occipital lobe is responsible for vision. Temporal lobe is concerned with hearing and smelling. Frontal lobe controls movement of skeletal muscles including movement involved in speech. Parietal lobe receive stimuli from skin and provides awareness of body position. The right and left hemispheres control the opposite sides of the body. The two hemispheres are connected by a bundle of nerve fibres called corpus callosum.
Thalamus is below the cerebrum. Thalamus receives nearly all impulses arriving from sensory areas of the body, before passing them to cerebrum. Thalamus is also involved in pain reception and consciousness.
Hypothalamus lies below thalamus. It regulates body temperature. appettie, water balance blood presure, feeling of mood etc. It links nervous system and endocrine system as it regulates the secretion of pituitary gland.
Just below the hypothalamus lies the pituitary gland. It is a very small gland about the size of a pea. It is an endocrine gland.
Midbrain
The midbrain is just a mass of tract below the cerebrum. The midbrain receive sensory information and sends it to the appropriate part of the forebrain. It also controls some auditory reflexes and posture.
Hindbrain
The hindbrain includes cerebellum, pons and medulla. Cerebellum is the second largest part of the brain. It control balance and muscle coordination. Medulla oblongata is the last part of the brain, just above the spinal cord. Medulla controls involuntary processes of the body like heartbeat, blood pressure and respiration etc. Medulla also controls reflexes such as coughing, sneezing and vomiting etc. Information is passed through medulla between the spinal cord and rest of the brain. Pons is small lobe like structure lying just above the medulla. It assists medulla in controlling breathing process. It also serves as a connection between cerebellum and spinal cord.
Spinal Cord
The human spinal cord is an oval shaped hollow cylinder of nervous tissue. It runs from the base of the brain. It is protected by the vertebrae of the backbone. 31 pair nerves originate from spinal cord. Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root of sensory neurons and ventral root of motor neuron. Therefore, all spinal nerves are mixed nerves. The spinal cord serves as a link between body parts and brain. It receives sensory information from the receptors and sends out motor commands to the effectors. The spinal cord works as coordinator. It carries out the reflex actions. It also helps in better functioning of brain.
The cross section of the brain and spinal cord shows that the central nervous system has two distinct areas.White matter consist of myelinated fibres. Grey matter is mainly cell bodies and non-myelinated fibres. In spinal cord butterfly shaped grey matter is surrounded by white matter. While in brain, grey matter makes up the outer layer having some white matter in the centre.
Peripheral nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nervous system with different body parts. Nerves which arise from brain are called cranial nerves. The nerves which arise from spinal cord are called spinal nerves. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves in the human body. Some cranial nerves are sensory, some are motor and some are mixed. While, all spinal nerves are mixed nerves.